News Archive
Filter by Division
Filter by Categories
The Path to Discovery
June 4, 2025 / Faculty SpotlightDr. Jennifer Brazil's Contributions to Inflammatory Bowel Disease Research
Colleen McDermott, MT(ASCP) Retiring
October 23, 2024 / Retirement30 Years of Service Coming to an End
Researchers find common immune system mechanism between pregnancy, cancer
July 8, 2024 / FacultyTo understand why some cancers successfully circumvent the immune system to grow unchecked, researchers turned to pregnancy.
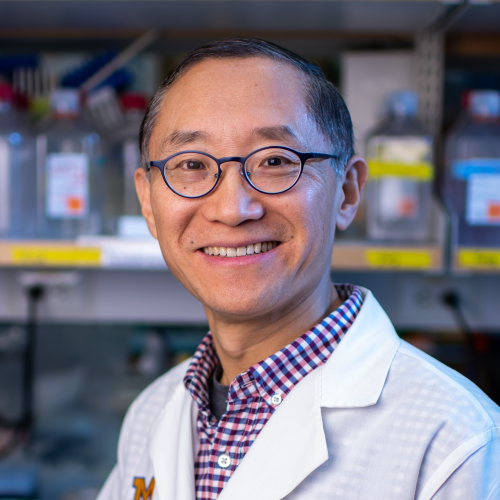 “In pregnancy, the immune system does not reject the growing fetus, so we know there must be mechanisms active in the placenta. In cancer, it’s the same thing: the growing tumor is not rejected by the immune system. It means the cancer cells have developed strategies to suppress immune rejection, same as in pregnancy,” said Weiping Zou, M.D., Ph.D., professor of experimental pathology.
“In pregnancy, the immune system does not reject the growing fetus, so we know there must be mechanisms active in the placenta. In cancer, it’s the same thing: the growing tumor is not rejected by the immune system. It means the cancer cells have developed strategies to suppress immune rejection, same as in pregnancy,” said Weiping Zou, M.D., Ph.D., professor of experimental pathology.
It’s a good thing in pregnancy – it allows the baby to grow. But in cancer, it means the tumor grows unchecked and treatments meant to stimulate an immune response are not effective.
MCP Graduate Student Michael Pitter Receives Trainee Abstract Award
October 16, 2023 / AnnouncementThe Department of Pathology invites you to join us as we congratulate our Molecular and Cellular Pathology Graduate Student, Michael Pitter, on being selected for the 2023 American Association of Immunologists Trainee Abstract Award. As the award recipient, Michael was invited to deliver an oral presentation at IMMUNOLOGY2023 in Washington DC.
A Passion for Helping Others Leads to a Career in Pathology
May 17, 2023 / Careers In PathologyDr. Xinna Li's story.
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Research Discovery Published
April 5, 2023 / ResearchA recently published research study led by Drs. Sem Phan and Tianju Liu from the Department of Pathology reported new findings that could help scientists predict disease progression and suggest a new immunotherapy target for the treatment of IPF and other fibrotic lung diseases.
These findings uncovered a new role for the immune checkpoint marker (B7-H3) in lung fibrosis that can potentially serve as a novel target for immunotherapy to slow down or abort the progression of lung fibrosis in patients with IPF and other chronic lung fibrotic diseases. In addition, sB7H3 levels in the plasma could serve as a potential marker to predict how quickly the disease progresses in patients and assess responsiveness to therapy, allowing for more informed treatment decisions.
Kim lab identifies the niche and mobilization mechanism for bone marrow innate lymphoid cell progenitors
January 25, 2023 / ResearchThe laboratory of Dr. Chang Kim, recently published a high-impact study that elucidates the bone marrow niche and mechanisms by which innate lymphoid cells differentiate between those which remain in the bone marrow and those which emigrate to the rest of the body. Read more[...]
Researchers Uncover Way to Harness the Power of Immunotherapy for Advanced Prostate Cancer
August 3, 2021 / BlogFindings offer clues to why some types of renal cell carcinoma respond to immunotherapy while others do not — it’s a scientific riddle tangled up in a complex web. How do you turn an immune cold cancer into one that responds to immunotherapy?
Role of BATF in the Development of Innate Lymphoid Cells Elucidated
February 10, 2021 / FacultyA series of sophisticated processes are required in the development of innate lymphoid cells (ILC) for them to reach maturity. The Kim laboratory discovered that basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor (Batf) regulates the production of ILC progenitors in the bone marrow as well as the maintenance of ILCs in the periphery. These cells are strategically distributed in peripheral tissues to provide important innate immunity to fight pathogens such as pathogenic viruses and bacteria.
New Study Finds Inhibition of Uric Acid or IL-1β Ameliorates Respiratory Syncytial Virus Immunopathology and Development of Asthma
April 15, 2020 / Experimental PathologyThe study details research surrounding Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) among infants.
Department Co-Hosts 2020 Mucosal Immunology Symposium
March 13, 2020 / Experimental PathologyThe event showcased experiemental pathology research.











 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
 ON THE COVER
ON THE COVER
